Scalable Collaboration of Multiple AI Agents in Workspaces
Ever wondered how to make AI agents actually useful in your daily work? While there’s been lots of buzz around AI automation, most solutions still struggle with a fundamental problem: they don’t fit naturally into how we actually work. That’s where SlackAgents comes in.
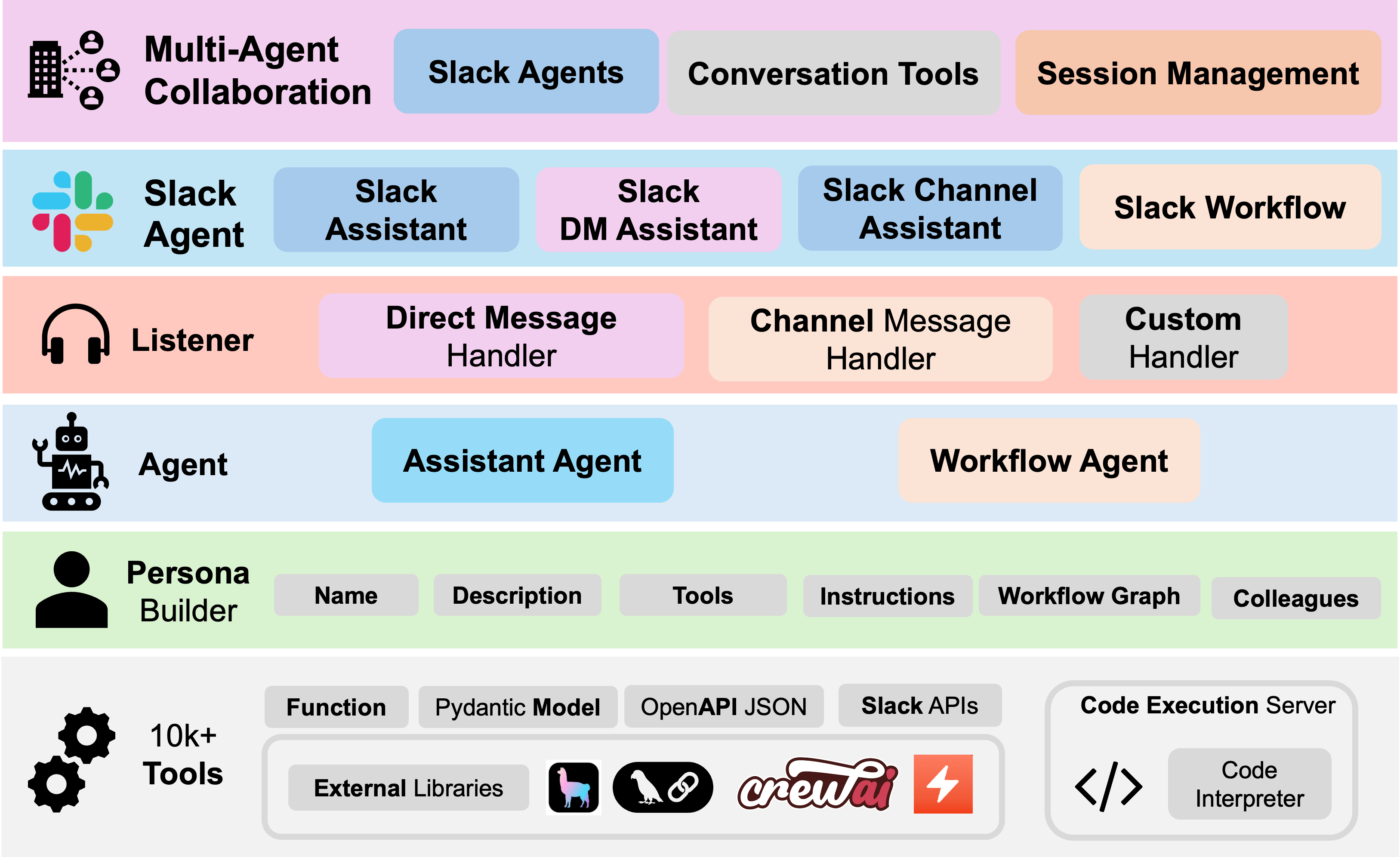
We present SlackAgents, a multi-agent library for scalable management and collaboration of AI agents on Slack. As an agentic layer developed upon the Slack platform, the framework offers instant AI integration into organizational workflows, enabling continuous improvement through daily use. It also leverages Slack’s extensive features to enable AI-powered automation of real daily tasks. Furthermore, SlackAgents facilitates scalable collaboration, allowing for effective communication and task orchestration. Our solution bridges existing gaps in AI agent management, offering a robust platform for developing, deploying and managing AI agents for workplace environments.
What Makes SlackAgents Different?
Here is a comparison of features supported by SlackAgents library vs existing libraries in terms of Multiple Agents: multi-agent orchestration; Workspace Automation: native Slack workspace feature support and automation; Scalable Collaboration: support for vast number of agents for collaborative task solving; Admin Management: interfaces for human supervisors to monitor and intervene; Market Distribution: instant deployment and distribution to workspaces via the Slack Marketplace.
| Library | Multiple Agents | Workspace Automation | Scalable Collaboration | Admin Management | Market Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LangChain | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| LlamaIndex | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| AutoGen | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| CrewAI | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| CAMEL | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| OpenAI Swarm | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| SlackAgents | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Our solution is a multi-agent library as an agentic layer leveraging the Slack infrastructure, the most widely used messaging and collaboration platform for corporate workspaces. The marriage of multi-agent framework with Slack can immediately bring the following benefits:
- Scalable Collaboration: multi-agent communication and task orchestration are handled by various types of conversation sessions across threads and channels of the Slack messaging system.
- Slack-Powered Automation: interfaces AI agents to various Slack features and visual components, such as canvas, bookmarks, workflows, notifications, etc., incentivizing developers to build AI agents that can control Slack for automating real daily work and tasks;
- Workspace Integration: enables developers to use every AI agent in the existing workflows, ensuring immediate deployment and continuous improvement through daily interactions. The agent can be easily distributed to the public and other Slack workspaces;

